Glulam
Floor & Roof Structure: MATERIALS ENCYcLOPEDIA
Applications for this system
Floor and roof framing
Basic materials
Dimensional lumber
Glue
Ratings Chart for glulam floors and roofs
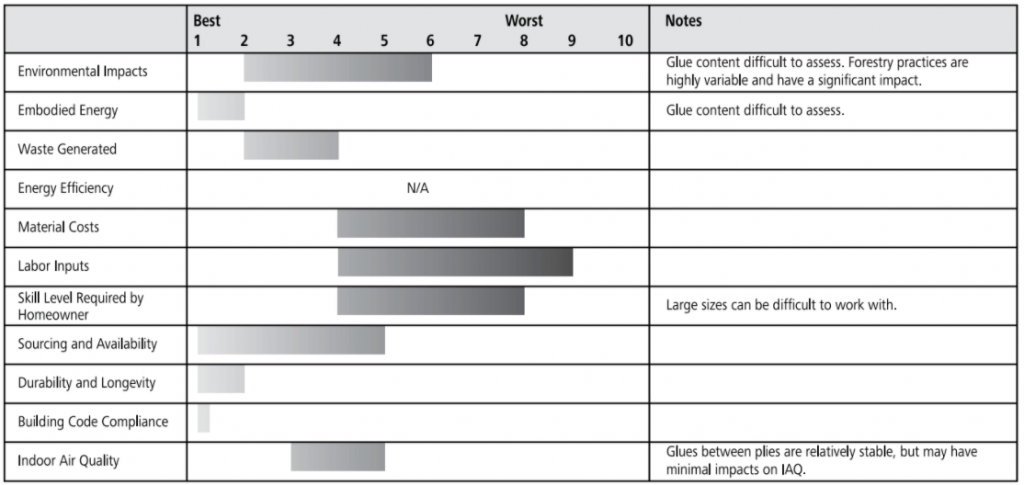
The ratings chart shows comparative performance in each criteria category. Click on the tabs below for detailed analysis of each criteria.
- HOW THE SYSTEM WORKS
- ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS
- WASTE
- EMBODIED CARBON
- ENERGY EFFICIENCY
- MATERIAL COSTS
- LABOUR INPUT
- SKILL LEVEL REQUIRED
- SOURCING & AVAILABILITY
- DURABILITY
- CODE COMPLIANCE
- INDOOR AIR QUALITY
- RESOURCES
- FUTURE DEVELOPMENT
Glulam System
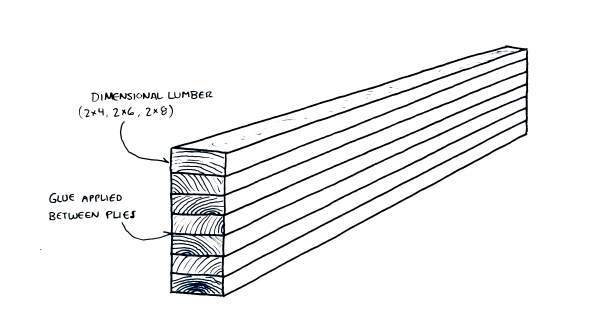 Lengths of dimensional lumber (2×4 and 2×6 are common) are stacked on their flat sides and glued together to create a continuous beam of the desired depth and strength. These glulam beams can be used horizontally as floor and ceiling framing, or in pitched applications — often in truss configuration — for roofs.
Lengths of dimensional lumber (2×4 and 2×6 are common) are stacked on their flat sides and glued together to create a continuous beam of the desired depth and strength. These glulam beams can be used horizontally as floor and ceiling framing, or in pitched applications — often in truss configuration — for roofs.
Glulams can be made in straight sections, but they can also be curved for vaulted applications, making them more adaptable to creative building shapes than any other structural system.
Environmental Impact Rating
Harvesting — Negligible to High
Unmanaged forestry can have impacts that include significant habitat destruction, soil erosion and ground water contamination. Third-party certification can help to ensure that impacts are minimized. Smaller diameter trees are required than for similar members of solid timber.
Metal fasteners may seem like a small component, but dozens of kilograms can go into a frame wall. Ore for steel production is mined in an intensive process with impacts including habitat destruction and soil and water contamination.
Glues for laminating are petrochemical based.
Manufacturing — Negligible to Moderate
The sawing and planing of structural lumber is a relatively low–impact mechanical process.
Processing raw ore into nails and screws is a multi-stage and intensive process requiring multiple infusions of high heat and fossil fuel use with impacts including air and water pollution.
Glues can have impacts including significant air and water pollution.
Transportation — Negligible to High
Sample building uses 2,945.5 kg of glulams for roof and floor framing:
4.4 MJ per km by 15 ton truck
2.8 MJ per km by 35 ton truck
Timber is a heavy and high-volume material and accrues significant impacts proportional to distance traveled. Regional manufacturers are accessible to many markets.
Installation — Negligible to Moderate
The number of offcuts from glulam beams can be quite high. Careful cut lists and ordering can minimize this waste.
Waste: Low to moderate
Landfill – Glulam offcuts
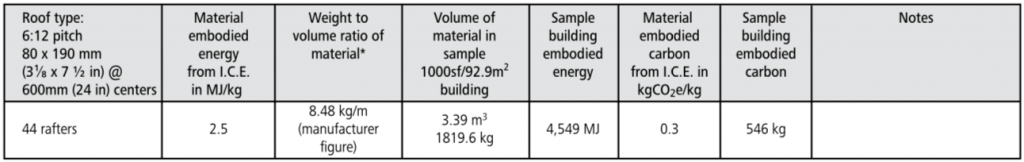
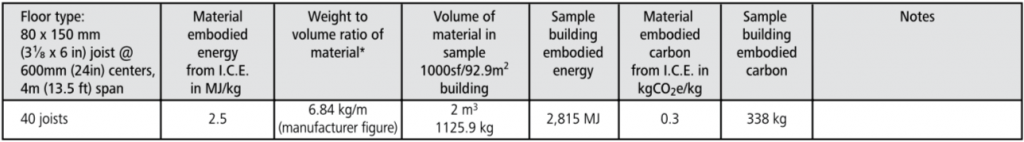
Chart of Embodied energy & carbon
glulam roof:
glulam floor:
Energy Efficiency
Glulams are typically used in scenarios where the beams/joists are exposed, and so any insulation strategy is usually accomplished on the outside of the glulam. Careful attention must be paid to keeping the insulation continuous at the roof/wall junction to prevent cold bridges or lesser levels of insulation. As long as the exterior insulation levels are suitable and the roof/wall junction detailed appropriately, the glulam won’t have any negative impact on energy efficiency.
However, because they are a solid timber, glulams can constitute a major thermal bridge if they are in contact with both the outside and inside face of the building. This type of use should be avoided, or an insulation strategy to address the bridging must be used.
Material costs: moderate to high
Glulams are typically more costly than open web style framing systems, as they use more wood to achieve high strengths, rather than geometry. However, they are often shallower in depth and this can result in lower building heights, creating savings on other materials in the total building enclosure.
Labour Input: moderate to High
Glulam beams and joists tend to be very heavy, and can require many hands and/or mechanical equipment to manage. When used as a roof framing system, cranes are often needed.
Large glulams on wide spacings are often used to replace systems in which smaller, lighter members are used at tighter spacings. By reducing the number of members, some labor savings can be achieved.
Once in place, glulams are usually fastened using prefabricated metal bracketry. This type of fastening can be quite easy to install, but placement needs to be accurate to ensure proper fit for the bracketry.
Skill level required for homeowners: moderate to high
Glulams are usually installed as part of a post and beam structure. Post and beam can be challenging for newcomers, and is usually the domain of experienced crews. Large frames require a degree of accuracy that can be challenging for beginners, and the work is often accompished by the use of booms or cranes that can be intimidating for those with no experience.
Sourcing & availability: Easy to moderate
There are fewer manufacturers of glulam beams than other manufactured joists, but they are available in most major markets. Some manufacturers offer standard dimensions that will be suitable for a range of projects, and these will be available when needed. Much of the market for glulams is for custom projects where the designer and the glulam manufacturer work together to create solutions for a particular need, and in these cases the lead times required must be part of the project planning.
Durability: High
Glulams are the oldest type of glued lumber product and have been in use since the 1950s. They have proven to be very durable over decades of service.
Code compliance
Glulams are a pre-engineered system, and are an accepted solution in most jurisdictions. Building departments will typically want to be provided with a signed, stamped version of the glulam drawings as part of the plan submission.
Indoor air quality
Several companies manufacture glulams using glues that have passed third-party testing by Greenguard, meaning that they meet stringent standards for IAQ. Unlike other glued wood products, the glue between each lamination has very little exposed surface area, minimizing contact between glue and the air or unintentional wetting.
Resources for further research
n/a
Future development
The widespread use of FSC or other third-party certified woods for glulams is likely to continue, making them more environmentally responsible. Glues have already been developed that meet high standards for indoor air quality, and new and better formulations will make glulams an even more attractive option.
Tips for a successful glulam floor or roof
1. Glulams are proprietary products, and each manufacturer will have its own installation guidelines that should be followed closely.
2. Notching, boring or altering a glulam beam should only be done in a manner approved by the manufacturer.